Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): A Retail Perspective
17/08/2021 | by Proximity

As the cyber-security standards are getting increasingly strict, we asked Achraf Chairi, Technical Analyst at Proximity Insight, to share a deep dive on the progression of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and the impact it has on the retail industry today.
Ever since Charles Babbage conceptualised the first computing machine in 1822, computers have revolutionised our planet and have proved to be increasingly powerful and vital to our society. Continuous developments showed the diverse utility of a computing system, from security and business to communication and amusement.
Nowadays, there is no limit to the power of technology and its potential. Every business and company interact in some way with computing systems, and technology. It is continuously changing and shaping our society. The scientific aspect of a computer’s establishment and the power of technology is very intriguing.
With such power, comes the responsibility of maintaining its security. If in the wrong hands, it could be used in a very malicious way. As new technology advances keep occurring, adversaries are getting more creative and have more tools in their possession in order to disrupt businesses and infiltrate systems.
Cyber Security is a vast field that constantly fits in our daily life. The understanding of its mechanisms, its management and its potential is extremely vital.
It is essential for businesses to uncover the many layers of the subject and establish a strong security foundation.
Now more than ever, because of the pandemic, security is crucial. Companies have started thinking about the way employees would work from home, especially when some companies deal with hyper-sensitive and confidential data & information. It was necessary to reinforce business systems as every employee working remotely is using their home network, which creates many liabilities and loopholes that can be exploited. In addition to standard security policies and infrastructure, Multi-factor authentication is a concept that has been on the rise in combating cyber-crime.
What is MFA?
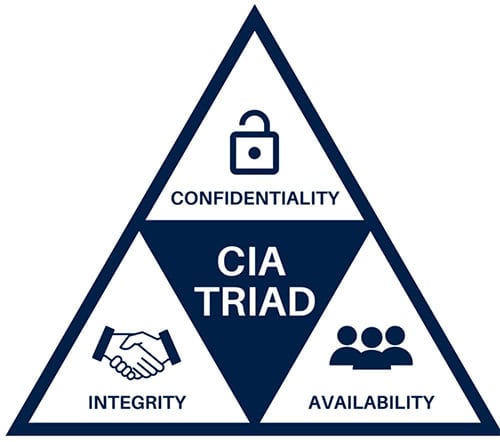
Multi-Factor authentication (MFA) is a mechanism that is essential for businesses in order to maintain the Cyber-Security CIA triad. This is the main concept that security is based on: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Any information security program that has one of these pillars compromised is not a secure program.
Confidentiality is associated with secrecy and the use of encryption. Only people who have permission to access, view or edit data are permitted to do so. The breach of confidentiality could either occur through hacking or social engineering.
Integrity means that data that is sent from/to the system is not modified or tampered with in transit. There are two points where Integrity could be compromised: During the upload of data or during the storage of data in the database. The Man-In-The-Middle attack is a very common way of disrupting integrity.
Lastly, Availability means that the asset is available to authorised users when it is needed. For a system to demonstrate availability, it must have properly functioning computing systems, security controls and communication channels. An example that can disrupt availability is a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack.
These three components are key for a safe and secure IT system. MFA is a mechanism that helps maintain and reinforce the safety and security of a system.
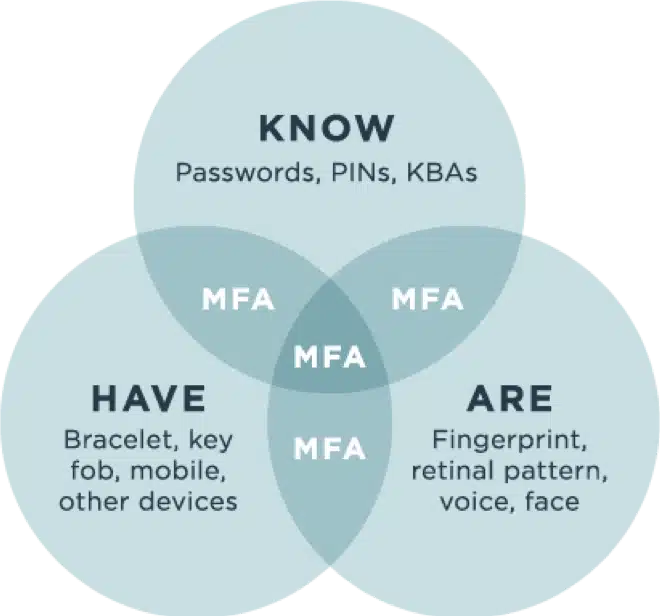
Multi-factor authentication, or MFA, as the name suggests, is about combining different factors upon authentication, specifically two or more factors.
There are 3 main factors:
- Knowledge Factor: This focuses on information the user knows. Typically, knowledge factor technologies include passwords, four-digit PINs, security questions and one-time passwords (OTPs). A scenario would be logging into a system with a username and password, and subsequently being asked to answer a security question.
- Possession Factor: The user must have a physical item in their possession upon authentication. This can be in the form of a key fob, a card, a badge, a token or a mobile phone. A scenario would be that the user has to open an authenticator on their phone to validate the authentication process.
- Inherence Factor: This factor includes any biological trait the user has. This can be in the form of fingerprints, facial recognition, retina or iris scan, voice authentication or digital signature scanners. A scenario using this factor could be that the user is asked to provide his fingerprint upon successful password entry, in order to be granted access to the system.
MFA and Retail
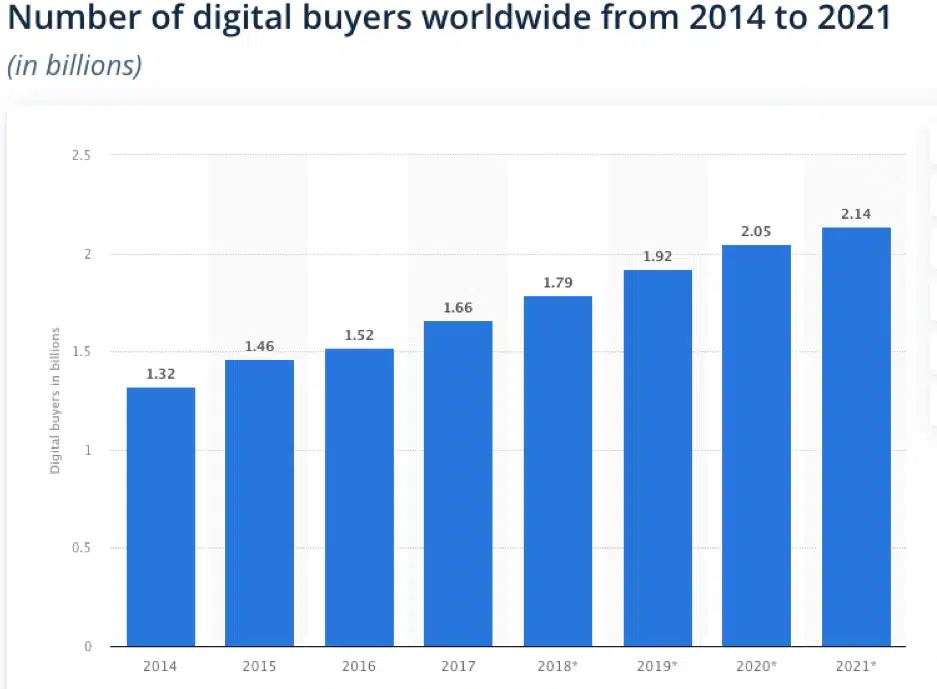
Traditionally, the majority of people used to shop in-store. Hence, MFA in retail was never a must. As the retail industry is becoming more and more digital, the demand for MFA within retail has been increasing. Some traditional retail companies are creating their e-commerce website to suit the needs of digital shoppers, while other companies focus solely on digital retail. Consumers prefer shopping with ease and convenience in mind. An order can be created and finalized within minutes, not requiring the customer to even move. This explains the exponential increase in the number of digital buyers worldwide (as seen in diagram below).
This has caused companies to start thinking about reinforcing their online business systems, to protect their customers’ data. If a breach is made, the adversary would access the customer’s name, address, and credit card information. A big liability was therefore discovered, and companies had to act fast. This is where MFA in retail came into place.
A recent Microsoft study conducted in October 2019 has uncovered that 59% of executives would have implemented or expanded MFA within the following three to six months. Another 26% would have done so within a year. Furthermore, according to Verizon’s 2019 Data Breach Investigations Report, 80% of hacking related breaches are attributed to weak or compromised passwords. MFA, requiring users to authenticate with at least two factors, can reduce the risk of identity compromise by as much as 99.9% over passwords alone.
Bad actors have been using compromised identities to gain a foothold in an organisation, avoiding detection for an average of 100 days. MFA is essential because it reduces the odds that two or more factors get compromised, hence reducing risks. 81% of respondents plan to increase their spending on MFA within retail.
The rules and regulations in retail are getting increasingly strict, and businesses must comply and obey the rules. There is a minimum standard that needs to be met by all companies processing online transactions. The PSD2 directive implemented in 2015 seeks to improve rules for electronic payments.
More specifically, it points out strict security requirements that shall be met by businesses that facilitate online payments. Its aim is to protect the consumer’s financial data, reducing the risk of fraud and guaranteeing safe authentication. With such regulation comes the need to secure the authentication process, using MFA within retail in particular.
Similarly, GDPR was published in 2016. It’s a legal framework that sets guidelines and processes for the collection and processing of personal data. This framework applies to Retail companies that have online shopping, because data about customers is held and shall be stored securely without the risk of breaching confidentiality or integrity.
According to a Javelin Strategy & Research Study, 70% of the survey participants feel secure purchasing items in-store, whereas only 56% of participants feel secure making an online purchase. Retailers can increase customer trust toward online transactions, by finding a balance between security and convenience. When it comes to online shopping, the need for security is essential as there is a lot of sensitive customer information that can put them in jeopardy both financially and physically. However, Consumers appear to be willing to spend more and more time in order to complete a transaction.
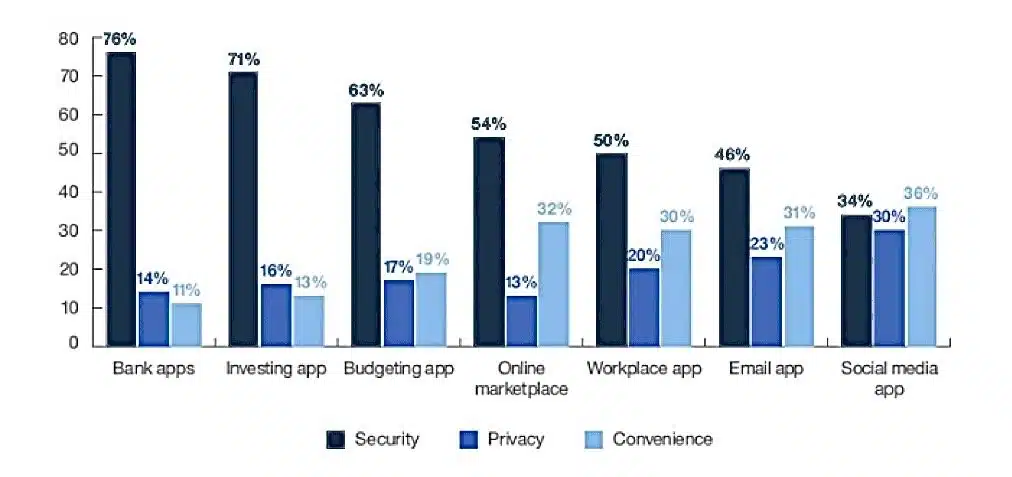
For instance, they are willing to spend extra time either inputting an OTP (One-Time-Passcode), or verifying their biometrics (Fingerprint, Face ID), to ensure a safe & secure transaction.
Nowadays, people are moving away from traditional sign-on methods such as passwords and are more open to use a set of authentication factors, to reduce the chances that an adversary might infiltrate the system using their details. The IBM Future of Identity Study 2018 reveals that people are becoming increasingly acceptant of new and unique authentication factors. Companies imposing an authentication method can lead to customer loss, and frustration. But laying out a set of identity verification methods that seem innovative and unique, might catch the customer’s attention, leading them to willingly accept it.
To conclude, dealing with customer data comes with a variety of risks. These risks can lead to a breach of confidentiality, integrity and/or availability. Security is therefore necessary in order to protect the infrastructure.
It is evident that multi-factor authentication is the go-to mechanism for creating extra-layers of security in order to guarantee the CIA Triad. In the retail sector, it is an authentication methodology that is increasingly apparent. The time has begun to focus on re-designing systems, with customer data being the focal point. Proximity Insight is implementing MFA upon authentication to the Proximity Insight Clienteling App. Security has always been a priority of ours so staying on top of these developments is essential. It is time to say goodbye to the traditional way of logging in using just a password.
To learn about Proximity Insight and our clienteling tool, follow us on LinkedIn or reach out to hello@proximityinsight.com